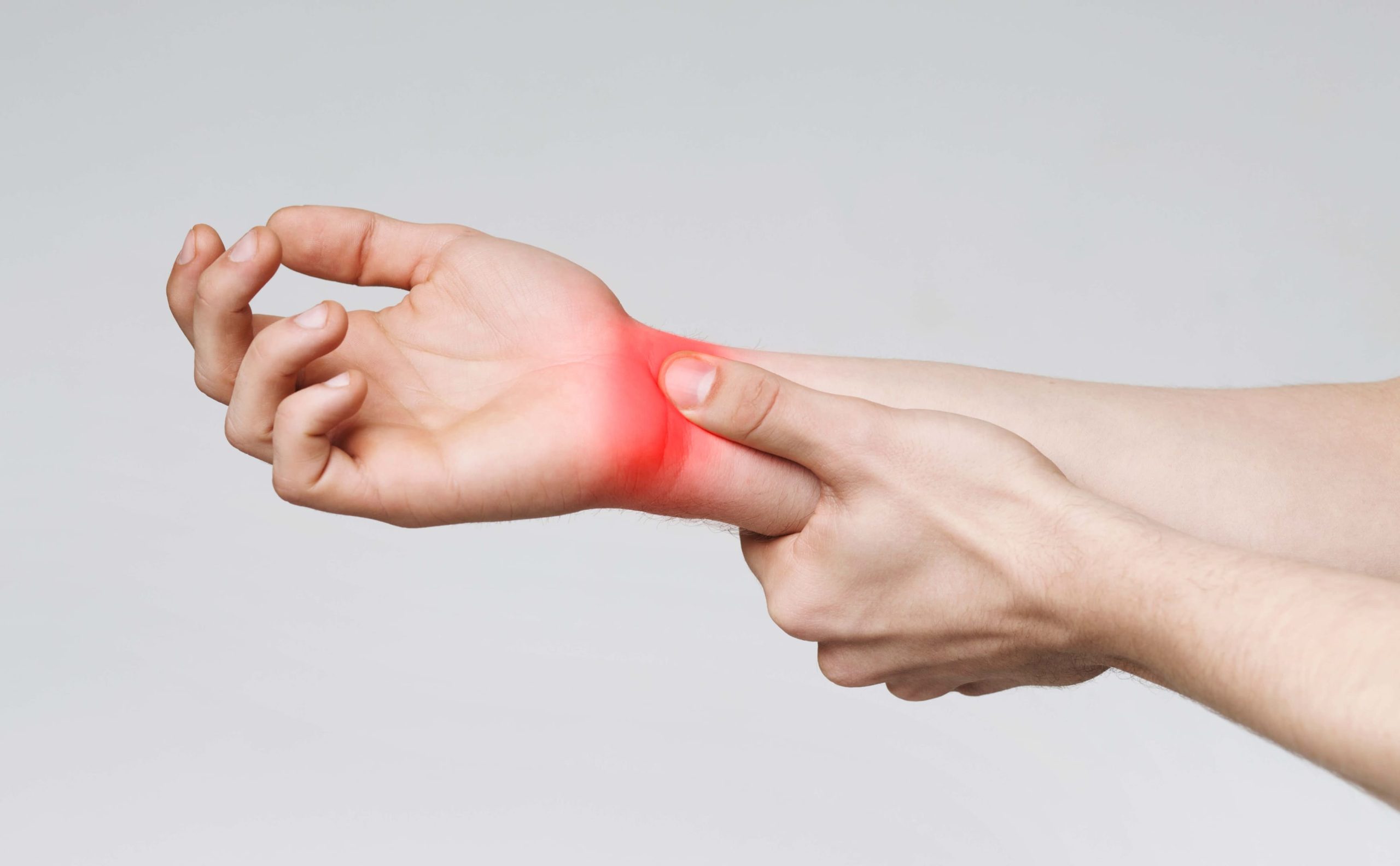
Carpal tunnel is the name given to a narrow tunnel in the wrist where the median nerve gets trapped. Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a debilitating condition affecting the hand, caused by impingement of the median nerve that innervates the digits of the hand.
Non-neutral position of the wrist increases the pressure on the median nerve within the carpal tunnel, which causes the development of the syndrome. That leads to pain, numbness, and a tingling sensation in the hand.
The prevalence of this nerve disorder is one in every three individuals. Women are at a higher risk of getting affected than men.
Table of Contents
Surgery
If untreated, CTS can progress into nerve damage, leading to permanent hand dysfunction. In severe cases, carpal tunnel surgery might be the most effective treatment to reduce pressure on the median nerve.
Carpal tunnel surgery is for severe and refractory cases where individuals don’t respond to conservative treatments. It involves surgical decompression of the nerve. Open carpal tunnel release (CTR) surgery is a highly effective treatment option. The surgeon cuts through the ligament to release the pressed nerve.
Causes and risk factors
Continuous repetitive movements like typing on a keyboard can irritate the median nerve. Studies show that office and factory workers (physical laborers) who work long hours with their hands, such as on assembly lines, are at a greater risk of developing CTS due to wrist overuse. Thus, taking measures to prevent health issues at desk jobs is crucial.
Symptoms
Individuals suffering from CTS patients typically experience typical nerve symptoms, including pain and numbness. The most common symptoms include:
Burning, tingling, and numbness
In most cases, the initial presentation of CTS is numbness of the hand. Some patients notice numbness after waking up in the morning, while others feel it when holding their phones. Individuals also report having altered or decreased sensations in the fingertips.
Wrist and thumb pain
Wrist pain ensues as the disorder progresses. Most patients notice a greater pain intensity during or after performing non-stop work with their hands. Pain induced by CTS is neuropathic and varies from individual to individual.
Research suggests that smokers experience more pain than non-smokers. Pain is a typical symptom of CTS but may be absent in some patients. The numbness is what might lead to a painful feeling.
Weakness of hand
Experiencing weakness of the hand is a common symptom of CTS. That leads to a compromised ability to grab small objects, hold heavy objects, and work on a computer.
Treatment Options
Treating Carpal tunnel syndrome depends on the severity of the symptoms. Early management of the symptoms by avoiding exerting pressure on the wrists and fingers can prevent the development of CTS and the need for surgery.
Non-surgical treatment
The main aim of the treatment is to decompress the median nerve. Some non-surgical interventions include.
Physical therapy
Physiotherapy reduces tendonitis and releases pressure from the nerve. Adding stretching and exercise to the routine can offer pain relief.
Wrist splints
Using braces/splints can relieve tension from the nerve. Most people wear wrist splints at night to return the wrist to a neutral position.
Steroid injections
In moderate to severe cases of carpal tunnel, corticosteroids are injected into the wrist to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Wrap up
Physical therapy, wrist splints, and steroid injections are effective non-invasive treatment strategies. Open carpal tunnel release is the most common and potent surgical treatment option for patients with severe CTS.